Blog | Reading Time 2 minutes
Poultry Microbiota Insight: Part 2 – Key role in digestion
Providing 5-30% of energy
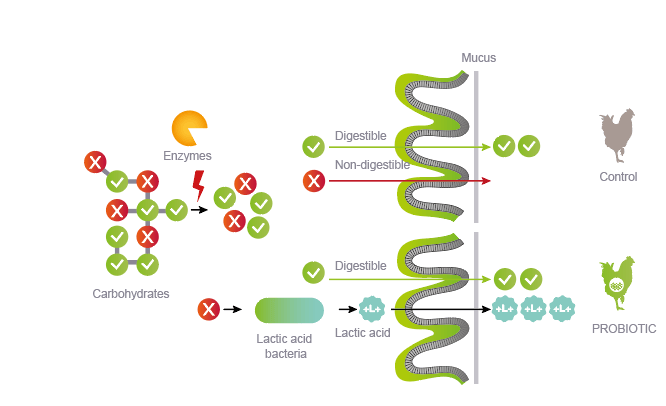
About 55-70% of a poultry feed formula is made up of cereals, the major source of carbohydrates, hence energy, for the birds. However, only simple carbohydrates such as starch are digested through an enzymatic process in the small intestine. The major part of complex carbohydrates and fibers present in the diet cannot be digested by the bird’s enzymes. Only certain microorganisms from the gut are able to digest these.
In the caecum, commensal microorganisms are able to hydrolyze the poly-, oligo- and di-saccharides into primary sugars. These are then further fermented into short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) and volatile fatty acids (VFA), which are mainly absorbed at the level of the caeca, providing additional energy to the bird.
It is estimated that the part of the total energy requirement for poultry coming from fermentation ranges between 5 and 30%, depending on the diet.
Supporting the digestive function
The gut microbiota not only takes part in energy metabolism but also influences the whole digestion process. Microbiota presence in the poultry gut also plays a role in intestinal absorption. The microbiota can be associated with:
- Increased villi height.
- Improved micronutrients absorption.
- Higher enzymatic activity.
The microbiota also plays a role in protein and lipid metabolism, vitamins and mineral absorption, also providing some of the essential nutrients that the host’s own enzymatic system is unable to produce (for example, vitamin K).
Practical implications
Many stress factors such as heat stress, sexing, feed transition, vaccination, pathologies, drugs, building transfer, etc., can affect the gut microbiota balance. As a consequence, growth and performance are affected.
Recent research has shown that feeding hens with a lactic acid bacteria known to balance the gut microbiota is able to improve feed efficiency and energy metabolism.
Published Oct 14, 2019 | Updated May 29, 2023
Related articles
Need specific information?
Talk to an expert