News | Reading Time 3 minutes
Deep diving into liquid feed hygiene: New study presented at the Pig Research Summit 2023
Our R&D and tech swine experts are gathering this week with the world’s leading experts in swine health and nutrition at the Pig Research Summit – THINK Piglet Health & Nutrition 2023, in Copenhagen, Denmark. In addition to exchanging about the latest trends and research in healthy pig nutrition, the team presented new data on the contribution of lactic acid bacteria Pediococcus acidilactici CNCM I-4622 to the hygiene of pig liquid feed. Let’s dive into this key topic!
Why is hygiene crucial in liquid feed?
In Europe, liquid feed is particularly popular for swine in countries including Denmark, The Netherlands, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, and Sweden, where more than 60% of finishers — as well as the majority of sows — are fed liquid feed.
Hygiene is key in liquid feed systems: the goal is to keep the feed at a low pH in order to limit the growth of undesirable microorganisms. Additionally, good feed hygiene has an effect on feed efficiency. In sows, for example, higher hygiene in the liquid feed is expected to increase milk production thanks to improved feed utilization, leaving more energy available for milk production. Ensuring the sanitary quality of liquid feed and the feeding system itself is a key priority in raising quality pigs.
How to ensure liquid feed hygiene for pigs?
The lactic acid bacteria strain Pediococcus acidilactici CNCM I-4622 (BACTOCELL), which was already marketed as a zootechnical feed additive with benefits on performance for piglets and fattening pigs, has recently been authorized in the European Union as a technological feed additive, in the categories of acidity regulator and hygiene condition enhancer. This lactic acid bacteria has been recognized for its potential to reduce pH and limit the growth of coliform bacteria in liquid feeds, offering an effective tool to help ensure liquid feed hygiene and quality.
The study presented at the Pig Research Summit aimed at monitoring the acidification and hygiene-enhancing properties of P. acidilactici CNCM I-4622 in pig liquid feed.
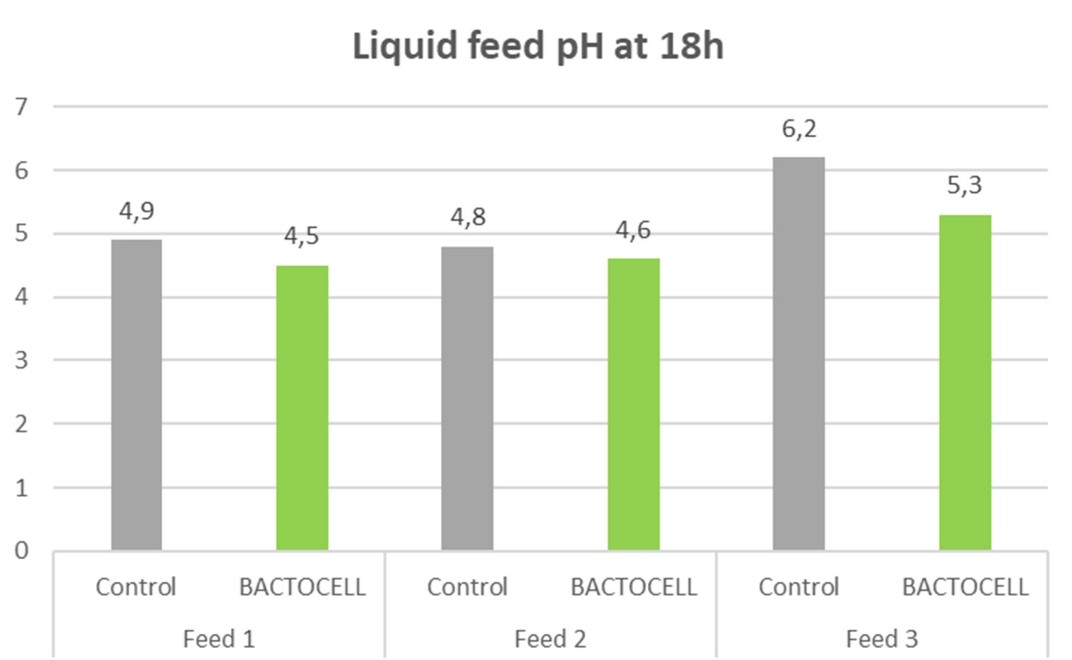
After 10 hours of incubation at 30°C, the feeds containing P. acidilactici CNCM I-4622 were better and faster acidified than the control feed. Feed pH remained significantly lower for up to 24 hours (Figure 1). Similarly, the concentration of L-lactic acid in the feed was significantly higher with the lactic acid bacteria.
Figure 1: Effect of P. acidilactici CNCM I-4622 on liquid feeds pH at 18 hours (n=3 feeds).
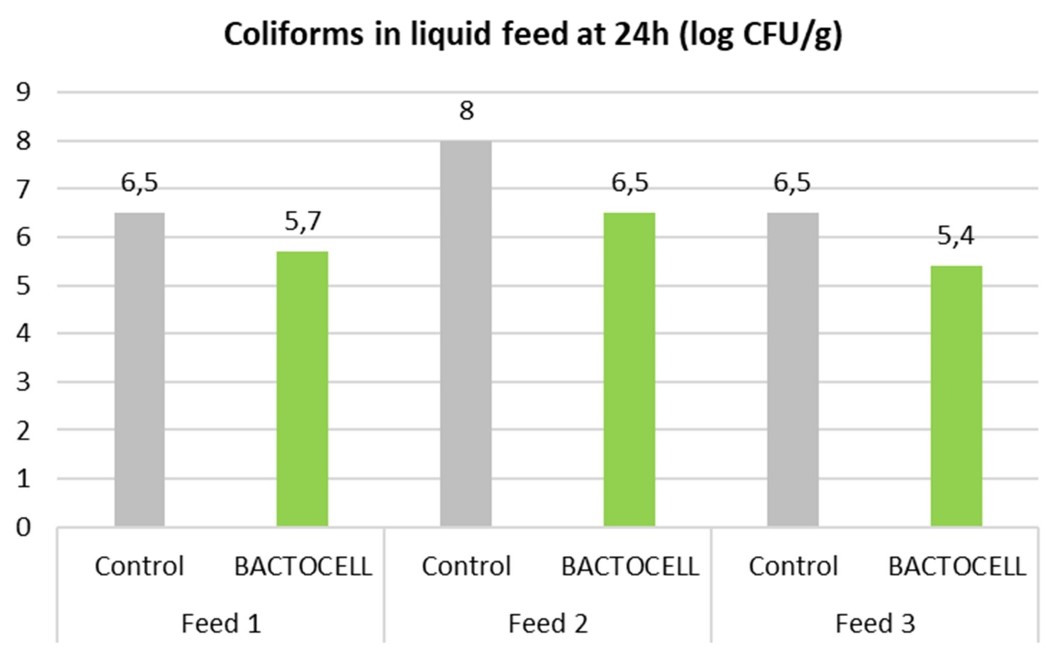
This enhanced lactic acid production ensured better feed hygiene as indicated by the significantly lower total coliform counts (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Effect of P. acidilactici CNCM I-4622 on liquid feeds total Coliforms count at 24 hours (n=3 feeds).
The researchers concluded that P. acidilactici CNCM I-4622 acidification properties contribute to the hygienization of pig liquid feed by reducing the development of total coliforms.
Consequently, P. acidilactici CNCM I-4622 could be considered as a tool to increase milk production of sows in liquid feed production systems, due to a potential improvement in feed efficiency.
REFERENCES
- Jacobs C., Hupé J.F., Pélissié I., Demey V., Saornil D., Bravo de Laguna F., Castex M. 2023 Potential of liquid feed hygienization by Pediococcus acidilactici CNCM I-4622 (MA 18/5M) to improve milk production. Pig Research Summit 2023, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Published Sep 20, 2023 | Updated Feb 28, 2024